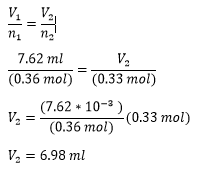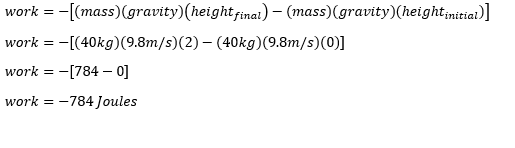I.
- A type of energy that cannot be created or destroyed?
Answer: Heat - States that the volume of a gas varies inversely with the pressure?
Answer: Boyle's Law - The most common practical use of the first law of thermodynamics?
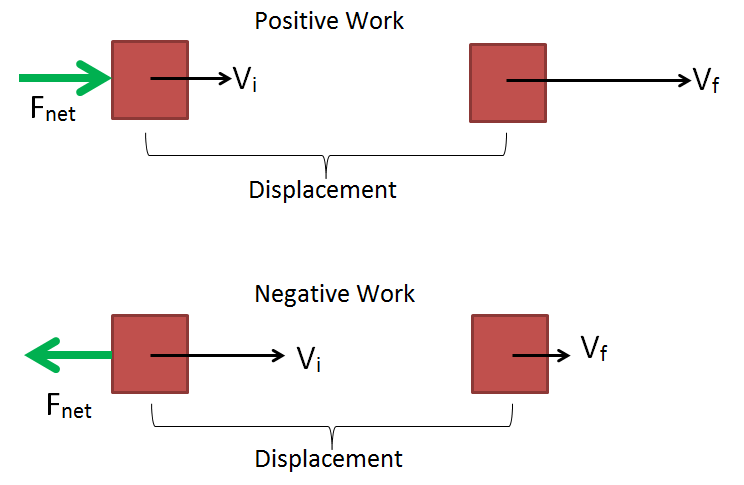
Answer: Heat engine - The energy transferred from the object is?
Answer: Negative work - When the object is stationary, its kinetic energy is?
Answer: Zero
II.
the initial position of the power supply is from the ground
- Being in the wrong place when an African elephant—mass = 6000 kg, velocity = 10 m/s—is charging can really ruin your day. How fast would a 10 kg cannonball travel if it had the same kinetic energy as the elephant?
Solution - A 30.0 L sample of nitrogen inside a rigid, metal container at 20.0 °C is placed inside an oven whose temperature is 50.0 °C. The pressure inside the container at 20.0 °C was at 3.00 atm. What is the pressure of the nitrogen after its temperature is increased to 50.0 °C?
Solution - A gas has a volume of 800.0 mL at −23.0 °C and 300.0 torr. What would the volume of the gas be at 227.0 °C and 600.0 torr of pressure?
Solution - If the spring is displaced for 75 cm and the work done to move the spring is --3.3 Joules, Find the spring force
Solution
- A Technician lifted a 1-kg power supply off the ground and it takes 5 seconds to move the power supply from the ground to the table that has a height of 1.2 meter
the initial position of the power supply is from the ground
so our initial height is Zero