What is kinetic energy?
Kinetic energy K is the energy associated with the state of motion of an object. The faster the object moves, the greater is its kinetic energy. When the object is stationary, its kinetic energy is zero but it will have potential energy.
The difference of kinetic energy and Potential Energy
kinetic energy is the energy that an object contains because of a particular motion. On the other hand, potential energy is the stored energy, because of its state of rest.
potential energy increases as weight and height increases
Examples of Kinetic Energy:
An airplane has a large amount of kinetic energy in flight due to its large mass and fast velocity.
Kinetic energy is not a vector. So a tennis ball thrown to the right with a velocity of 5 m/s, has the exact same kinetic energy as a tennis ball thrown down with a velocity of 5 m/s.
Example problem
What is the Kinetic energy of 145 g baseball with a velocity of 42.5 m/s?
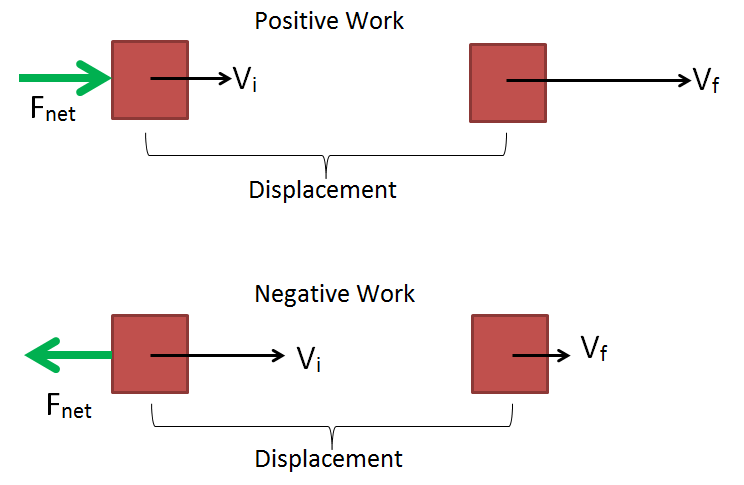
In Physics, work is the displacement of an object due to force.
Work done by gravitational force
Work done by spring force
Work done by a variable force
Work done by spring force
Work done by a variable force
These three topics include forces and displacement so they are considered as subtopics for work. I also included the topic of Power in terms of work
We already know that
For the gravitational force, we consider the change of
distance in terms of y-axis
So the equation should be
The gravity is always downward
So we can say that the work done by a gravitational force is
negative in every opposing force
Example problem
A mechanic lifts a 40-kg engine off the ground at a constant speed of 3m/s.
after the engine is lifted 2 meters, calculate the work done by the gravitational force
Solution
the initial position of the engine is from the ground
so our initial height is Zero
Work done by spring force
where:
k=is the spring force
most of the spring force problems the initial value at 0 m
therefore, our equation will be
Example problem
find the work done of a spring having a spring force of 200 N/m if the spring is compressed 0.025 meter?
Given
spring constant=200N/m
Distance=0.025
Work done by variable force
Example problem
find the work done to lift a 20 kg from the floor to a height of 3 m when the variable force f(x) is given in newtons.
Given force
Solution
Power in terms of work
Power is the rate of doing work or using energy
Example problem
It takes 12000J of work to lift an elevator to the 3rd floor of a building ,if this is done in 8 seconds what is the rate of work?
Solution
it takes 1500 watts to lift the elevator to the 3rd floor
https://www.khanacademy.org/science/ap-physics-1/ap-work-and-energy/kinetic-energy-ap/a/what-is-kinetic-energy






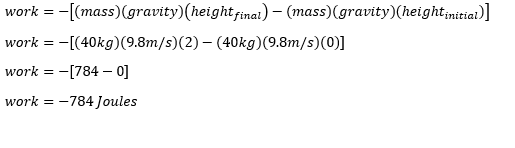








No comments:
Post a Comment